Heat Pumps: A Sustainable Heating Solution for the UK

As the world grapples with the urgent need to combat climate change, sustainable energy solutions are beginning to take centre stage. Fossil fuels have had their day – we simply cannot carry on digging for oil and gas when our world is drastically warming. Here, in the UK, where heating and cooling systems account for a significant portion of energy consumption, heat pumps are emerging as a promising technology that not only provides efficient temperature control but one that will also help to mitigate environmental impacts. Here we are going to explore what heat pumps are, how they work, and why they are better for the environment.
What Are Heat Pumps?
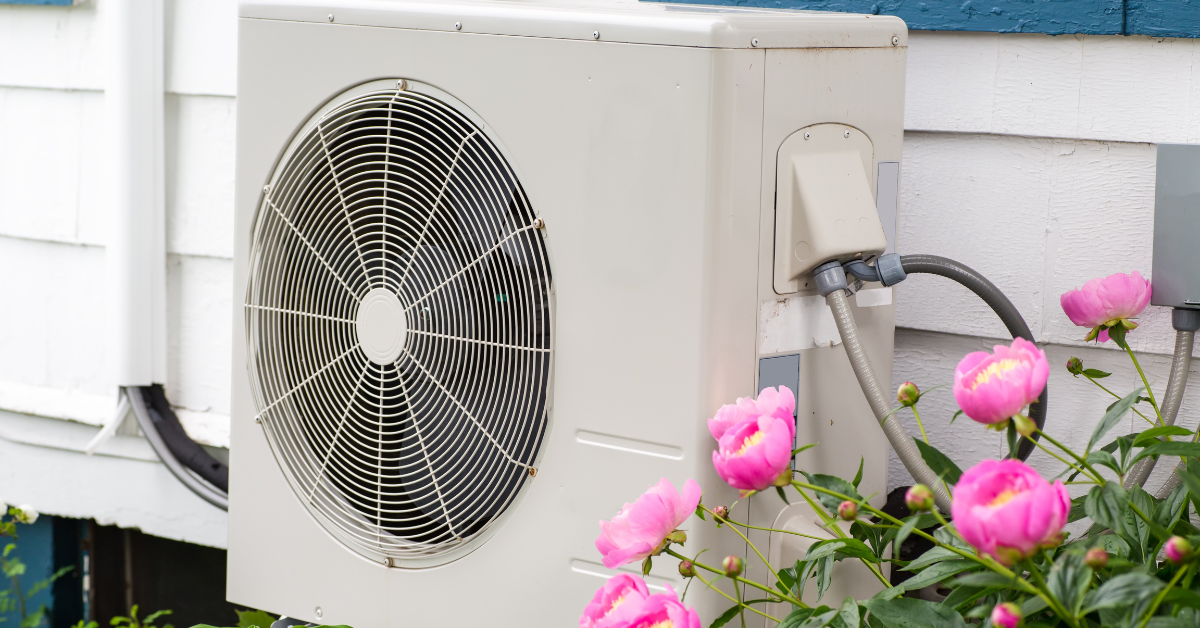
Heat pumps are innovative devices that use a simple yet effective process to transfer heat from one place to another. They can be used for both heating and cooling applications, making them versatile solutions for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures – something we could all benefit from, what with the UK weather being the way it is. Unlike traditional heating systems that rely on burning fossil fuels, heat pumps move heat from a low-temperature source to a higher-temperature location.
How Do Heat Pumps Work?
Over to the technical stuff… Heat pumps operate on the principle of thermodynamics, utilising the natural movement of heat from warmer areas to cooler ones. Here’s a basic overview of how they work:
- Absorption or Compression: There are two main types of heat pumps: absorption and compression. Compression heat pumps are the most common and work by compressing a refrigerant gas to raise its temperature. Absorption heat pumps use a heat-absorbing medium, typically a solution of water and ammonia.
- Evaporation and Condensation: Both types involve a cycle of evaporation and condensation. In the evaporation stage, the refrigerant (or heat-absorbing medium) evaporates, absorbing heat from the surroundings. In the condensation stage, the refrigerant releases heat as it condenses back into a liquid.
- Heat Transfer: The heat pump extracts heat from an external source, such as the air, ground, or water, and transfers it indoors for heating or removes heat from indoors for cooling. This process is highly efficient because it requires minimal energy input compared to conventional heating systems.
Why Are Heat Pumps Better for the Environment in the UK?
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: One of the most compelling reasons heat pumps are better for the environment is their significantly lower carbon footprint. In the UK, where a substantial portion of energy consumption is still derived from fossil fuels, heat pumps offer a cleaner alternative. They can run on electricity, which can be generated from renewable sources like wind, solar, or hydroelectric power, further reducing emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, with some models boasting a coefficient of performance (COP) greater than 4. This means they can provide four times the heating or cooling energy compared to the electrical energy they consume. Improved energy efficiency translates to lower energy bills and reduced strain on power grids.
- Reduced Air Pollution: Since heat pumps do not rely on combustion, they do not produce harmful emissions or indoor air pollutants, making them a healthier choice for homes and businesses. This reduction in air pollution has a direct positive impact on the overall air quality in the UK.
- Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI): The UK government has introduced the Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI), a financial incentive scheme that rewards homeowners and businesses for installing renewable heating systems, including heat pumps. This makes heat pump installations more cost-effective and therefore should hopefully accelerate their adoption.
- Versatility: Heat pumps can be integrated into various heating and cooling systems, including underfloor heating, radiators, and forced-air systems. Their adaptability makes them suitable for both residential and commercial applications, contributing to a broader reduction in carbon emissions.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
- Reduce your home’s CO2 emissions
- Lower running costs
- Low maintenance
- Safer than a gas boiler
- Long life-span
Downsides of Heat Pumps
- You need significant outdoor space/garden area for one to be installed. Underground units will require more disruptive work to your home
- Condenser units can be noisy
- They are only carbon-free IF your electricity is all sourced via renewable energy
- High upfront cost (although with a grant this will significantly help)
- Require planning permission
As you can see, the advantages do outweigh the disadvantages and as heat pumps really are a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution these are something that most of us should be considering.
For more information and to get a range of quotes check out the GreenMatch website.